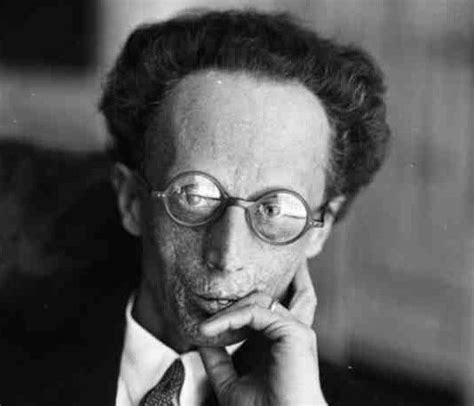
A Quote by William Whewell
According to the technical language of old writers, a thing and its qualities are described as subject and attributes; and thus a man's faculties and acts are attributes of which he is the subject. The mind is the subject in which ideas inhere. Moreover, the man's faculties and acts are employed upon external objects; and from objects all his sensations arise. Hence the part of a man's knowledge which belongs to his own mind, is subjective: that which flows in upon him from the world external to him, is objective.
Related Quotes
It is alone that part of the external universe which we call material which acts on man through his senses - that part of which we ordinarily feel our knowledge to be the surest; but in reality, strangely enough, as will soon appear, this is one of the aspects of the external world, of which we can know nothing.
Knowledge is inherent in man; no knowledge comes from outside; it is all inside. We say Newton discovered gravitation. Was it sitting anywhere waiting for him? It was in his own mind; the time came and he found it out. All knowledge that the world has ever received comes from the mind; the infinite library of the universe is in our own mind. The external world is simply the suggestion, the occasion, which sets you to study your own mind.
[I]f a man bred to the seafaring life, and accustomed to think and talk only of matters relating to navigation, enters into discourse upon any other subject; it is well known, that the language and the notions proper to his own profession are infused into every subject, and all things are measured by the rules of navigation: and if he should take it into his head to philosophize concerning the faculties of the mind, it cannot be doubted, but he would draw his notions from the fabric of the ship, and would find in the mind, sails, masts, rudder, and compass.
Man is more than his environment. It is from the innate quality of the Spirit in him, his inner storehouse, that he draws those ideas, his intuitions, which unify his perceptions of the external world instantaneously with a value which is qualitative and not quantitative, and which he embodies in the works of his culture - those achievements which belong not only to one particular time but to all times, and mark the path of his upward progress.
How very seldom do you encounter in the world a man of great abilities, acquirements, experience, who will unmask his mind, unbutton his brains, and pour forth in careless and picturesque phrase all the results of his studies and observation; his knowledge of men, books, and nature. On the contrary, if a man has by any chance an original idea, he hoards it as if it were old gold; and rather avoids the subject with which he is most conversant, from fear that you may appropriate his best thoughts.
Pathology has made us acquainted with a great number of states in which the boundary lines between the ego and the external world become uncertain or in which they are actually drawn incorrectly. There are cases in which parts of a person's own body, even portions of his own mental life - his perceptions, thoughts and feelings -, appear alien to him and as not belonging to his ego; there are other cases in which he ascribes to the external world things that clearly originate in his own ego and that ought to be acknowledged by it.
It is not a slight thing, gentlemen, to force a man to say what he is, or what he believes himself to be; for that supreme word of man, that single expression which he utters of and upon himself is decisive. It lays down the basis upon which all judgment of him is to be formed. From that moment all the acts of his life must correspond to the answer given by him.
It is thus that the generality of mankind, whose lot is ignorance, attributes to the Divinity, not only the unusual effects which strike them, but moreover the most simple events, of which the causes are the most simple to understand by whomever is able to study them. In a word, man has always respected unknown causes, surprising effects that his ignorance kept him from unraveling. It was on this debris of nature that man raised the imaginary colossus of the Divinity.
There's one uneasy borderline between what is external and what is internal, and this borderline is defined exactly by the sense organs and the skin and the introduction of external things within my own body. Consciousness is altered by physical events and physical objects, which impinge upon my sense organs, or which I introduce into my body. Now the name traditionally given to external objects or processes which change you internally is sacrament. Sacraments are the visible and tangible techniques for bringing you close to your own divinity.
Philosophers have very justly remarked that the only solid instruction is that which the pupil brings from his own depths; that the true instruction is not that which transmits notions wholly formed, but that which renders him capable of forming for himself good opinions. That which they have said in regard to the intellectual faculties applies equally to the moral faculties. There is for the soul a spontaneous culture, on which depends all the real progress in perfection.
The work of the inventor consists of conceptualizing, combining, and ordering what is possible according to the laws of nature. This inner working out which precedes the external has a twofold characteristic: the participation of the subconscious in the inventing subject; and that encounter with an external power which demands and obtains complete subjugation, so that the way to the solution is experienced as the fitting of one's own imagination to this power.
Man never ceases to seek knowledge about the objects of his experiences, to understand their meaning for his existence and to react to them according to his understanding. Finally, out of the sum total of the meanings that he has deduced from his contacts with numerous single objects of his environment there grows a unified view of the world into which he finds himself "thrown" (to use an existentialist term again) and this view is of the third order.
[Man] is the only animal who lives outside of himself, whose drive is in external things—property, houses, money, concepts of power. He lives in his cities and his factories, in his business and job and art. But having projected himself into these external complexities, he is them. His house, his automobile are a part of him and a large part of him. This is beautifully demonstrated by a thing doctors know—that when a man loses his possessions a very common result is sexual impotence.