Top 1200 Subject Matter Quotes & Sayings - Page 3
Explore popular Subject Matter quotes.
Last updated on April 17, 2025.
What I found interesting in dance is the idea that my work has always been dealing with the nervousness between the human subject as a subject and the human subject as a form. And if you look at my dance films, there are always these cuts between the dancer as a form, the dancer as a subject, and this kind of very harsh treatment of the dancer as someone who's actually drawing with their body.
I think you reveal yourself by what you choose to photograph, but I prefer photographs that tell more about the subject. There's nothing much interesting to tell about me; what's interesting is the person I'm photographing, and that's what I try to show. [...] I think each photographer has a point of view and a way of looking at the world... that has to do with your subject matter and how you choose to present it. What's interesting is letting people tell you about themselves in the picture.
Cognitive states of mind are seldom addictive, since they depend upon exploration of the world, and the individual encounter with the individual object, whose appeal is outside the subject's control. Addiction arises when the subject has full control over a pleasure and can ponder it at will. It is primarily a matter of sensory pleasure, and involves a kind of short-circuiting of the pleasure network. Addiction is characterized by a loss of the emotional dynamic that would otherwise govern an outward-directed, cognitively creative life.
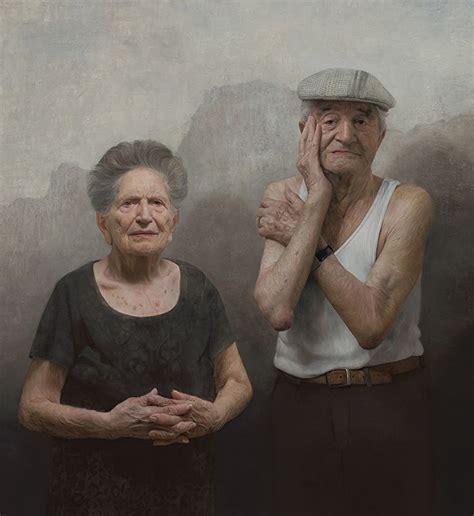
I want my paintings to give the viewer a true sense of reality - that includes but is not limited to depth, scale and a tactile surface as well as the real sense of what the subject looks like and is feeling at the time that I painted them. There should be a discourse between the viewer and the subject, to feel as though they are in a way connected. My goal is not to set a narrative but rather to have the viewer bring their own experiences to the painting and the subject as they would if they had seen the subject on the street in real life.
Confronted with the loving-sharing Consensus of subject-SUBJECT relationships all Authoritarianism must vanish. The Fairy Family Circle, co-joined in the shared vision of non-possessive love - which is the granting to any other and all others that total space wherein each may grow and soar to his own freely-selected, full potential - reaching out to one another subject-to-SUBJECT, becomes for the first time in history the true working model of a Sharing Consensus!
Desire is a word I'm tired of. I've been living with that word for years. Yes, of course, we're all desiring machines. I have sometimes wondered what people would want, if there were no advertising. And death, what other subject is there? It's the subject. It's our subject. It's the great human dilemma, that we die and know we will.
Well, I think there was a time when I first started that there was such a thing called 'a woman's film' and there were certain scripts that women would make. But I think that's changed a lot now. I think that if a woman director walks into a room with a script, it doesn't really matter what the subject matter is, or the genre is, so long as the financiers feel that the woman has the skills to make the film.
There was a time when I first started that there was such a thing called 'a woman's film' and there were certain scripts that women would make. But I think that's changed a lot now. I think that if a woman director walks into a room with a script, it doesn't really matter what the subject matter is, or the genre is, so long as the financers feel that the woman has the skills to make the film.