A Quote by Joan Robinson
The fundamental differences between Marxian and traditional orthodox economics are, first, that the orthodox economists accept the capitalist system as part of the eternal order of Nature, while Marx regards it as a passing phase in the transition from the feudal economy of the past to the socialist economy of the future.
Related Quotes
My Prime Minister regards the economy as our highest priority and forgets that economics and ecology are derived from the same Greek word, oikos, meaning household or domain. Ecology is the study of home, while economics is its management. Ecologists try to define the conditions and principles that enable a species to survive and flourish. Yet in elevating the economy above those principles, we seem to think we are immune to the laws of nature. We have to put the ‘eco’ back into economics.
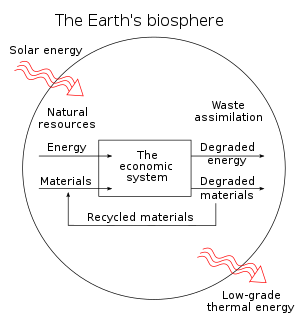
The laws of thermodynamics restrict all technologies, man's as well as nature's, and apply to all economic systems whether capitalist, communist, socialist, or fascist. We do not create or destroy (produce or consume) anything in a physical sense- we merely transform or rearrange. And the inevitable cost of arranging greater order in one part of the system (the human economy) is creating a more than offsetting amount of disorder elsewhere (the natural environment).
Capitalism is very far from a perfect system, but so far we have yet to find anything that clearly does a better job of meeting human needs than a regulated capitalist economy coupled with a welfare and health care system that meets the basic needs of those who do not thrive in the capitalist economy. If we ever do find a better system, I'll be happy to call myself an anti-capitalist.
I think capitalism will not disappear, but it's going to increasingly not be the exclusive arbiter of economic life. It's going to have to find value in interacting with the sharing economy on many levels. And this hybrid system that's already emerging among millennials is going to be a mature system where, by midcentury, part of the day will be in the capitalist market, part of the day in the sharing economy, depending on your marginal costs.
In the last few decades we have seen the extraordinary rise of ecosocialist movements around the world inspired in large part by Marx's ecological critique of political economy. Marx was indeed influenced by some of the earliest attempts to develop what we now call an ecological-systems view, rooted in the concept of metabolism. Building on this perspective, Marx defined socialism as the rational regulation by the associated producers of the metabolism between society and nature in such a way as to conserve energy and to promote the satisfaction of human needs.
Our practical choice is not between a tax-cut deficit and a budgetary surplus. It is between two kinds of deficits: a chronic deficit of inertia, as the unwanted result of inadequate revenues and a restricted economy; or a temporary deficit of transition, resulting from a tax cut designed to boost the economy, increase tax revenues, and achieve -- and I believe this can be done -- a budget surplus. The first type of deficit is a sign of waste and weakness; the second reflects an investment in the future.